Intrusive Lyric Intelligibility (ICASSP Cadenza)
The Challenge
The Cadenza ICASSP 2026 Challenge tasked systems to predict lyric intelligibility rates from perceptual experiments on accompanied singing, including simulated hearing loss. The main difficulty was building an intrusive model that accounts for acoustic quality, lexical alignment, and contextual cues in music mixtures.
My Role & Collaborators
I was responsible for the key orchestration, planning, and delivering results for the entire project. Our team from Aalto University secured 2nd place in the final evaluation rankings.
Our Solution
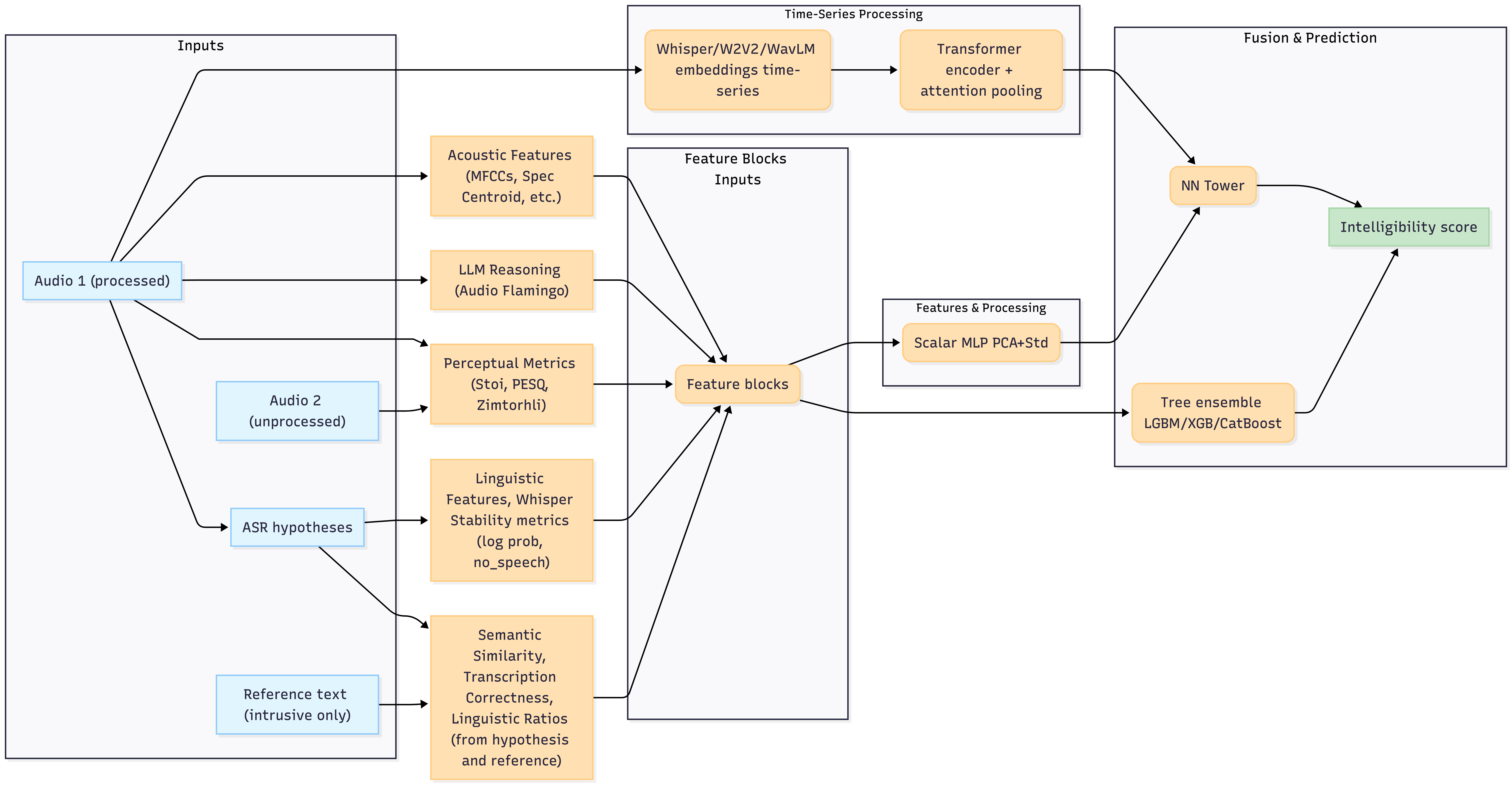
We built a system (T071a) that combines a hybrid neural mixture of experts (WavLM/Wav2Vec2/Whisper) performing attention pooling over time-series embeddings, fused with tree-based regressors (LightGBM, XGBoost, CatBoost). Scalar feature blocks summarized intrusive perceptual metrics (STOI, PESQ, Zimtohrli), ASR stability, and linguistic complexity. A multi-modal LLM (Audio Flamingo) score provided human-like rating priors.
Key Techniques
- Hybrid Neural Mixture of Experts (WavLM/Wav2Vec2/Whisper)
- Tree-based Regressors (LightGBM, XGBoost, CatBoost)
- Intrusive Perceptual Metrics (Zimtohrli, STOI)
- Multi-modal LLM scoring (Audio Flamingo 3)
- Attention Pooling
Project Links
Results
The system achieved a Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) of 0.265 and Normalized Cross-Correlation (NCC) of 0.69 on the official evaluation set, ranking 2nd place.
System Architecture